#Rich Text field
The RichText field type is an advanced String field that returns your content in 4 different formats by default: raw, HTML, markdown, and text. JSON is also available when embeds are enabled.
The Rich Text field renders an advanced textarea with tools to add headings, links, tables, images, lists, etc.
When a Rich Text field is added to your model, it will automatically generate the following types:
type RichText {raw: RichTextAST!html: String!markdown: String!text: String!json: RichTextAST!}
#Rich Text data
Let's talk about Rich Text data in more detail.
-
Raw:
rawAST (Slate Nodes) offers complete control over how nodes are presented to the user. -
JSON:
JSONrepresentations of RTE allows as much control asrawdoes, but offers the possibility of creating embeds.RichTextwill include the fieldJSONin addition torawonly if Rich Text Embeds are enabled. BothJSONandraware aliases, but if you have embeds enabled you should ideally useJSON. -
HTML:
HTMLcan be used with a Rich Text renderer for customization purposes. While rendering the HTML of your rich text is simple, it doesn't offer great customization. -
Markdown:
Markdown- likeHTML- can be used for customization. Whilemarkdownis easier to read and write - specially for users without a technical background - it's not as expressive asHTML. To presentmarkdownon a page, you'll need amarkdownparser that will convertmarkdowntoHTML. -
Text:
textis mostly used for excerpts, as links, images, and even line breaks are removed.
#Use Cases
- Raw: Use
rawwhen you want to control the rendered output using our render libraries. - JSON: Use
JSONfor the same asrawbut when you also need embeds. - HTML / Markdown: Use these when you need to make customizations and want to insert pre-built
HTMLormarkdowninto an app. - Text: Use
textwhen you want to provide the text as data to a script, such as making full-text search.
#Examples
This section takes a simple Rich Text piece with a title, a paragraph, a link, and bold text, and offers its JSON, HTML, Markdown, and Text representations.
#Rich Text embeds
If Rich Text Embeds are enabled, RichText will include the field JSON in addition to raw.
For example, we can query all of those on our RichText field type content:
#Embed assets
You can also embed Assets and other models inside Rich Text as block, inline or link embeds.
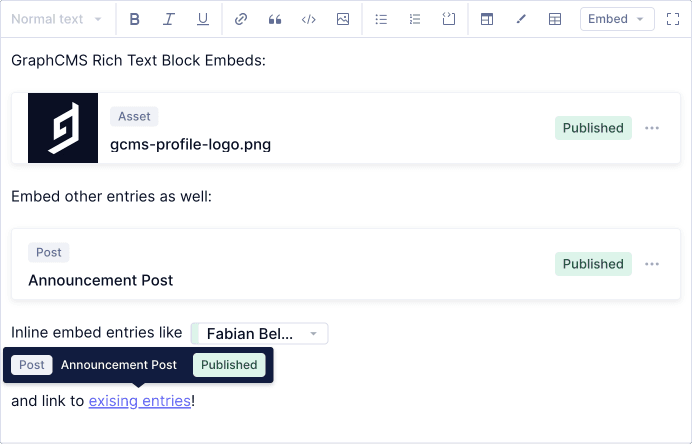 Rich Text Asset Embeds UI
Rich Text Asset Embeds UI
You can find out how to enable Rich Text embeds in our field configuration docs.
#Rich Text embeds & API types
With Rich Text Embeds enabled, your API will have some new types added. The name of your field will be now a type appended by RichText, and RichTextEmbeddedTypes inside your schema.
For example, if you had the model Post and field content, the types generates would be PostContentRichText, and PostContentRichTextEmbeddedTypes respectively.
The PostContentRichText type will look like the following:
type RichText {json: RichTextAST!html: String!markdown: String!text: String!references: [PostContentRichTextEmbeddedTypes!]!}
The references field will be a union relation to the types you embedded, for example Asset.
You should use the references field when querying JSON to get the URL - with any transformations, handle, or any of the Asset fields.
The HTML response will return gcms-embed-type and gcms-embed-id data attributes for the embedded types. A block embed is returned as div and an inline embed as span with a data-gcms-embed-inline attribute. A link embed is returned as an a-tag with a data-gcms-embed-id and data-gcms-embed-type attribute.
Hygraph uses Slate 0.5 for RichTextAST.
If you are programmatically creating content entries with Rich Text, you should use the @graphcms/html-to-slate-ast package.
#Use JSON representation of RTE for customization
You can work with the Rich Text field to take the data that the editors put in Hygraph, and manipulate it for display in the front end.
The following example shows data available on a blog post, with the Rich Text content in HTML and markdown:
Hygraph automatically serializes the content into HTML and/or markdown that the front end can simply display. This does not allow customization.
Instead of these two things, you can get the JSON representation, which will display as JSON AST in a tree with nested levels.
Remember that Richtext will only include the field JSON if Rich Text embeds are enabled for the model you're using.
As you can see in the results tab of the above query, this breaks up the initial data into a JSON representation that a renderer can understand.
This allows you to take that data and manipulate it in order to override any default renderer or add renderers for custom elements, creating a custom display logic for your front end.
You will do this by creating an HTML element containing the manipulated data, which will then be rendered via the astToHtmlString method that's available on our Rich Text HTML renderer. We also have a React version of this.
Click here to access a detailed example on how to style Rich Text using TailwindCSS.
By styling your Rich Text fields, you can either customize how your Rich Text will display throughout your website, or even have multiple types of Rich Text fields that do different things.
#Resources
- Hygraph's Rich Text editor: Hygraph's UI Rich Text field feature walkthrough.
- Styling Rich Text with TailwindCSS: Detailed tutorial on how to use the
JSONrepresentation from the RTE to create custom elements for each text-based element of Rich Text. - Introducing the Hygraph React Rich Text Renderer: Blog post on how to render Hygraph documents using Rich Text in your application easily using our available packages.
- Rich Text editor UI guide: Guide on how to use Hygraph's Rich Text editor in the content editor of your project.