#Overview
Filtering allows you to use specific parameters to restrict the entries that display in a content table. This is helpful when trying to create a more curated overview of content.
These filters can be useful when building content views, looking for a specific type of content, or finding content that matches several parameters.
 Filters
Filters
#Quick Filters
Our Quick Filters feature reduces the time and effort required to create a filter. You can now find the content you need, faster.
 Quick Filters
Quick Filters
It offers several predefined filters that apply instantly when selected, allowing you to focus on you work without unnecessary distractions.
Pro Tip
You can apply Quick Filters to both regular content views and asset views.
To add Quick Filters, simply use the Filter menu to display the available options and select one.
 Add a Quick Filter
Add a Quick Filter
Once you select a Quick Filter, the regular filter appears in the filter bar and the content table shows the sorted content.
You can apply more than one Quick Filter. To do this, simply use the filter menu again and select another one.
For instance, the following image shows a content table where two Quick Filters have been applied, Created by me & Only published entries:
 Quick Filter applied
Quick Filter applied
#Column filters
The Filters menu also contains column filters.
 Column filters
Column filters
Column filters allow you to filter content by some system and custom fields, stage and ID.
Quick and column filters function in the same way. The following document section explains how to use them.
#Adjust filters manually
You can find the filters on any content view, at the top of the content table. Clicking on the Filters menu displays your options for quick and column filters:
 Filters menu
Filters menu
You can use the Search at the top of the filters menu to quickly find a filter.
To filter content, select one of the fields listed for filtering. It can be a quick or column filter:
- If you selected a quick filter, the results will show on the table below.
- If you selected a column filter, you need to configure it:
At the moment, you can't use these filters for components, union type references, or Rich Text.
To remove a filter, simply click the X button next to it.
#How to use system filters
#Stage
 Filter content by stage
Filter content by stage
- Click
Filter to open the filter menu.
- Select
Stage from the column filters list.
- Use the dropdown menu next to
Stage to pick a condition.
- Select a stage from the second dropdown menu.
For example, if you select is on the first dropdown, and then PUBLISHED on the second, the filter will show you all the content entries that are currently on the PUBLISHED stage.
It is not necessary to type in a keyword in the search field for this filter to work, so you can use the filter on its own to return search results on all the content in that model, or you can use it to narrow down a search that uses keywords.
An ID is a unique identifier of your content entry that the system assigns to it when you first save it. You can see it on the sidebar in the edit view, under Entry information.
 Content entry ID
Content entry ID
If you know the ID of a content entry you are looking for - totally or partially - you can use that to quickly find it using the ID filter.
 Filter content by ID
Filter content by ID
- Click
Filter to open the filter menu.
- Select
ID from the column filters list.
- Use the dropdown menu next to
ID to pick a condition.
- Enter a value in the text field next to the conditions dropdown.
Some examples
Imagine we are looking for a content entry with the ID clgm2kql0bspm0burfoqjqhdl:
- If you know the exact ID, you could simply use
is clgm2kql0bspm0burfoqjqhdl as a filter. This would return only one result, the exact content entry you're looking for.
- If you know the the ID starts with
clgm, you could use starts with cglm as a filter. This would return all content entries that have IDs that start with cglm.
- If you know the ID ends in
qhdl, you could use ends with qhdl as a filter. This would return all content entries that have IDs that end with qhdl.
#Created / Updated at
The Created at and Updated at filter look at DateTime fields in the content entry. This can be the date of creation/update, as well as any DateTime field in the schema configuration for the model.
 Filter content by Created at
Filter content by Created at
The DateTime field contains date/time information at UTC, which would look something like this 2007-12-03T10:15:30Z. Since this information is extremely exact, it is best to use the Created at filter with the less than or greater than conditions.
- Click
Filter to open the filter menu.
- Select
Created at, or Updated at from the column filters list.
- Use the dropdown menu to pick a condition.
- Enter a value in the calendar field next to the conditions dropdown.
#Created / Updated / Published by
These filters take a list of project users, and compare a value you provide to relational fields in the project, so - in a way - this would be filtering by relations.
 Filter content by Created by
Filter content by Created by
This filter functions like so:
- Click
Filter to open the filter menu.
- Select
Created by, Updated by, or Published by from the column filters list.
- Use the first dropdown menu to pick a condition, and the second one to enter or select a value. These are reference filters, and you can find detailed information about their usage here.
#Filters and your schema
While all projects have the default system filters, different filters may display depending on your project schema configuration.
Let's go over this with an example. Look at the following project schema for a Product model:
 Filters example: The Schema
Filters example: The Schema
It has fields for product name, slug, image, sections, description, price, a condition, an enumeration for product size, and a taxonomy for product category.
When you go to the Content editor section of the app, select the Product view, and click on the Filter menu, you will see most of the fields you saw in the schema as filters under "Column Filters", in addition to the system filters that are always there.
 Filters example: The Content Editor
Filters example: The Content Editor
Some fields, such as rich text, can't be filtered in the content editor and require a different approach through the API Playground which, in turn, requires familiarity with GraphQL, and is not usually Editor work.
#General filter conditions
In general, a filter will provide different conditions depending on the type of field configured in the schema. You will find string, boolean, enums, taxonomy, reference, and DateTime.
Each type offers different conditions to filter by:
#String
Strings are sequences of characters, so they are often used for text fields such as titles or descriptions. They offer the following conditions for filtering:
is: This condition filters for content that matches the text you enter.is not: This condition filters for content that doesn't match the text you enter.contains: This condition filters for content that contains the text you enter.doesn't contain: This condition filters for content that doesn't contain the text you enter.starts with: This condition filters for content that starts with the text you enter.doesn't start with: This condition filters for content that doesn't start with the text you enter.ends with: This condition filters for content that ends with the text you enter.doesn't end with: This condition filters for content that doesn't end with the text you enter.
An good example of this type of filter that you can find in all projects is the ID filter.
#Boolean
Boolean fields can take two values: true and false. In all cases, booleans provide a condition dropdown, and then a second dropdown containing the true / false values.
The conditions dropdown menu for booleans contains the following options:
is: This condition filters for content that matches the value you select from the dropdown.is not: This condition filters for content that doesn't match the value you select from the dropdown.is null: This condition filters for content where no value has been assigned to the field. You do not need to select any value for this filter.is not null: This condition filters for content where a value has been assigned to the field. You do not need to select any value for this filter.
For example, imagine you have a boolean for reviewed. Like all booleans, it can only take two values: true & false. So, if you set the filter to reviewed is true, the filter will return all entries where the reviewed boolean field has been set to true.
#Enum
Enums are lists of items. Your project has them as system fields, like in the case of content stage, and may also have them as custom dropdown fields in the schema.
In all cases, enums provide a condition dropdown, and then a second dropdown containing the values configured on the list for that enum. Like this:
 Taxonomy - example
Taxonomy - example
The above example shows a filter where the enum is a list for product sizes. This particular field allows multiple values, so you have checkboxes next to every option in case you need to select more than one.
The conditions dropdown menu for enums contains the following options:
is: This condition displays content that is an exact match for the value you select from the dropdown.is not: This condition displays content that is not an exact match for the value you select from the dropdown.is null: This condition displays content where no value has been assigned to the field. You do not need to select any value for this filter.is not null: This condition displays content where a value has been assigned to the field. You do not need to select any value for this filter.includes all: This condition displays content that matches all the values you select from the dropdown.includes none: This condition displays content that matches none of the values you select from the dropdown.includes some: This condition displays content that matches some of the values you select from the dropdown.
Please note that not all enums will display all the options above, some may display them partially. An example of this is the Stage filter.
#Taxonomy
A taxonomy is a group of terms arranged in a hierarchical structure. Your project has them as system fields and may also have them as custom dropdown fields in the schema.
In all cases, taxonomies provide a condition dropdown, and then a second dropdown containing the values configured for that taxonomy. Like this:
 Taxonomy - example
Taxonomy - example
The above example shows a filter where the taxonomy is a category for product types.
The conditions dropdown menu for taxonomies contains the following options:
is: This condition displays content that is an exact match for the taxonomy node you select from the dropdown.is not: This condition displays content that is not an exact match for the taxonomy node you select from the dropdown.is in: This condition displays all content that matches the multiple taxonomy nodes you select from the dropdown.is not in: This condition displays all content that does not match the multiple taxonomy nodes you select from the dropdown.descendants of: This condition displays content that matches the selected taxonomy node and all nodes below it.
#Reference
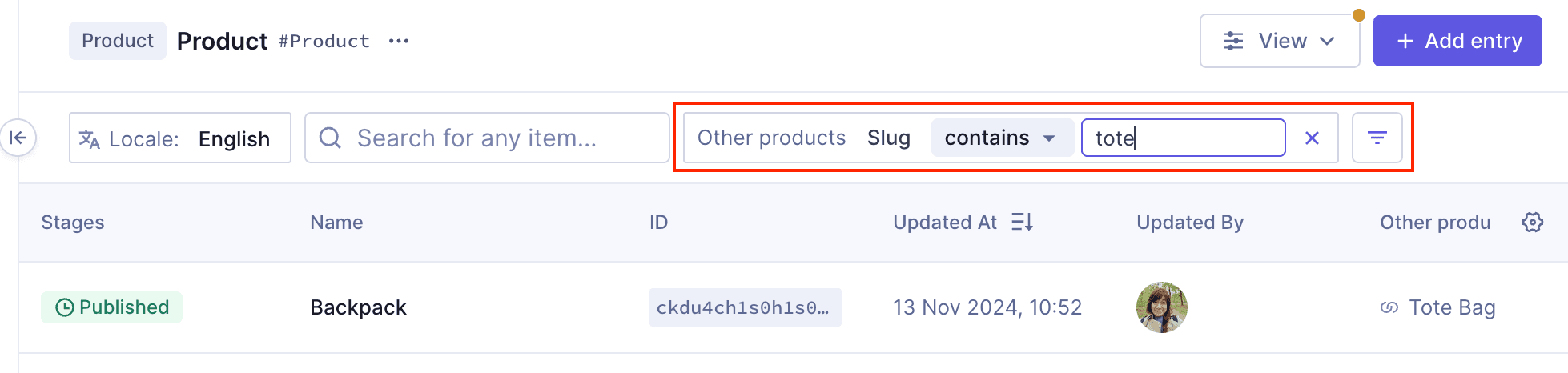 Filtering by relations
Filtering by relations
Filtering by reference is basically filtering by relation. This filter is dynamic, in the sense that it changes depending on the relational field you select, but in general terms its usage follows three steps:
- Select the field of this model that you want to use.
- Select a condition from the dropdown menu.
- Some conditions will require that you type in some data to filter by, such as a name or a slug.
Updated At and Created At require that you select a date from a calendar and type in a time. Is null and Is not null do not require any additional input.
It is not possible to filter by union-type reference fields - those that allow you to reference more than one model in a field.
The references you can select for your filter depend on project configuration. All projects have the default reference filters - we'll look into them in a moment - but they can also have a number of custom ones.
The default reference filters that all projects have are Created by, Updated by, and Published by. They are related to project users and provide the following relational fields that you can select from the dropdown:
IsActive: IsActive checks if the user is active or not. This is a boolean field and, as such, it offers all conditions a boolean field does, and you will be able to select true or false from the values menu.Kind: Kind is an enum field that checks if the creator of a piece of content is a user or a token. As most enum fields, it offers all conditions an enum field does, and you will be able to select one of the following values from the values menu:
MEMBER: The content was created / updated by a user.PAT: The content was created / updated by a token.PUBLIC: The content was created / updated by the public API.WEBHOOK: The content was created / updated by a webhook.APP_TOKEN: The content was created / updated by an app.
Picture: This checks for pictures of the related users. This is a string field and, as such, it offers all conditions a string field does, and allows you to enter text to apply that condition to.Name: This checks for names of the related users. This is a string field and, as such, it offers all conditions a string field does, and allows you to enter text to apply that condition to.Updated At: This checks for date and time of update of a content entry. This is a DateTime field and, as such, it offers all conditions a DateTime field does, and allows you to select a date and time from a calendar picker.Created At: This checks for date and time of creation of a content entry. This is a DateTime field and, as such, it offers all conditions a DateTime field does, and allows you to select a date and time from a calendar picker.ID: This checks user IDs. This is a string field and, as such, it offers all conditions a string field does, and allows you to enter text to apply that condition to.
#DateTime
The DateTime field contains date/time information at UTC, which would look something like this 2007-12-03T10:15:30Z.
This field type offers the following conditions:
is: This condition returns exact matches to the date and time selected, including milliseconds. Considering this filter won't provide results unless the information provided is exact, it is recommended to stick to less than and greater than conditions for date & time.is null: If your project has custom fields for date & time, and these fields are not required, then they may not always have a value assigned to them. If this is the case, using the is null filter returns all content entries where that custom date & time field does not have a value.is not null: This condition returns all content entries that have a value assigned to a date and time field.is not: This condition returns all entries where the date & time is not the one you provide.less than: This condition returns all entries where the date & time is earlier than the one you provide.less than or equal to: This condition returns all entries where the date & time is earlier than or equal to the one you provide.greater than: This condition returns all entries where the date & time is later than the one you provide.greater than or equal to: This condition returns all entries where the date & time is later than or equal to the one you provide.
An example of this that you can find in every project are the Created at and Updated at filters.















